Definition
They share electrons, and neither give nor take them. So better we both share the things that we need.
Single Covalent Bond
 In dot structure, it is represented like in the left side, the right side is the Lewis Structure, which is much simplified.
In dot structure, it is represented like in the left side, the right side is the Lewis Structure, which is much simplified.
Double Covalent Bond
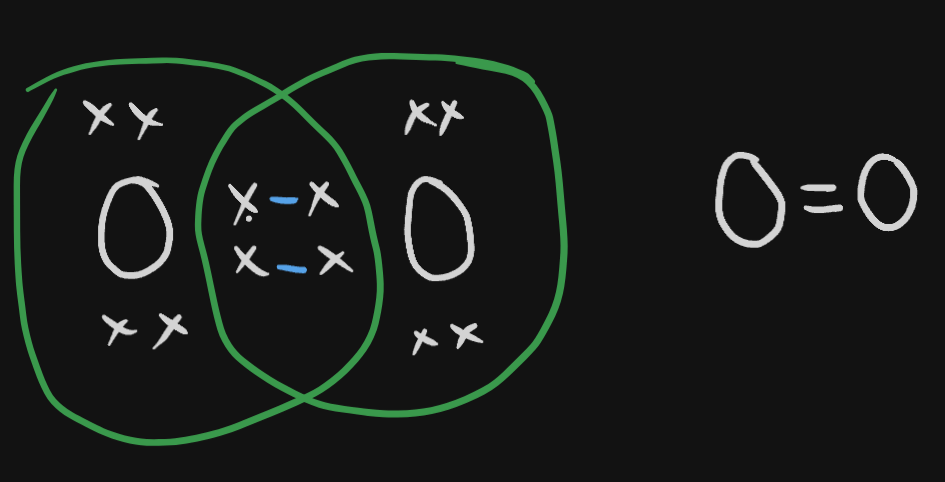 In a dot electron structure, the valence electrons are displayed. Bonds are made based on the electrons they need to share in order to get it.
Each bond is represented by a dash in Lewis Structure.
In a dot electron structure, the valence electrons are displayed. Bonds are made based on the electrons they need to share in order to get it.
Each bond is represented by a dash in Lewis Structure.
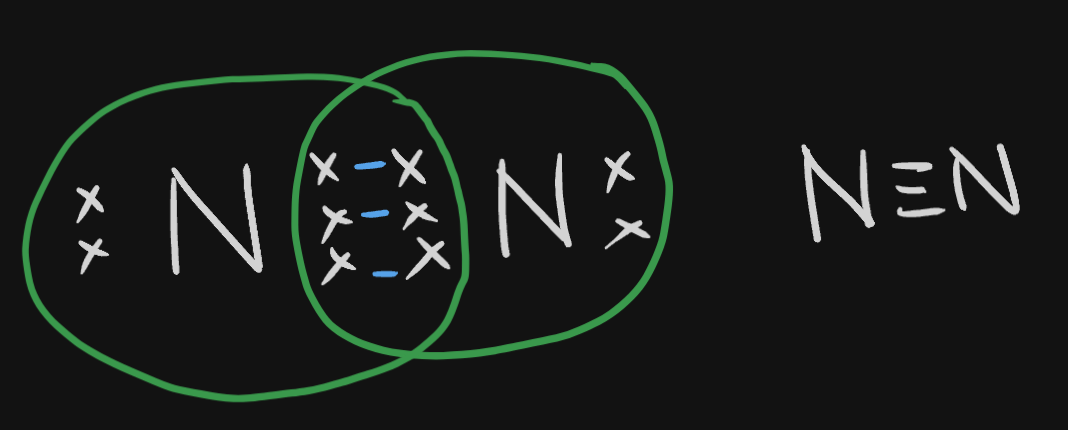
Triple Covalent Bond
Tetravalency
Carbon, and other similar elements possess a property of tetravalency, meaning, they have 4 valence electrons and share electrons. Why?
- Giving away 4 electrons introduces instability between protons and elections.
- Taking 4 elections also introduces instability between protons and elections.
Characteristics of Covalent Compounds
Antithesis of Ionic Compounds
- They have weak bonds
- They have low melting and boiling points
- They are insoluble in water and soluble in benzene, petrol, kerosene, etc.
- They do not conduct electricity (because they do not produce free ions.)
Backlinks
Flashcards
What is a covalent bond? ? They share electrons, and neither give nor take them.
What is tetravalency? ? Carbon, and other similar elements possess a property of tetravalency, meaning, they have 4 valence electrons and share electrons.
What are the properties of covalent compounds? ?
- They have weak bonds
- They have low melting and boiling points
- They are insoluble in water and soluble in benzene, petrol, kerosene, etc.
- They do not conduct electricity (because they do not produce free ions.)